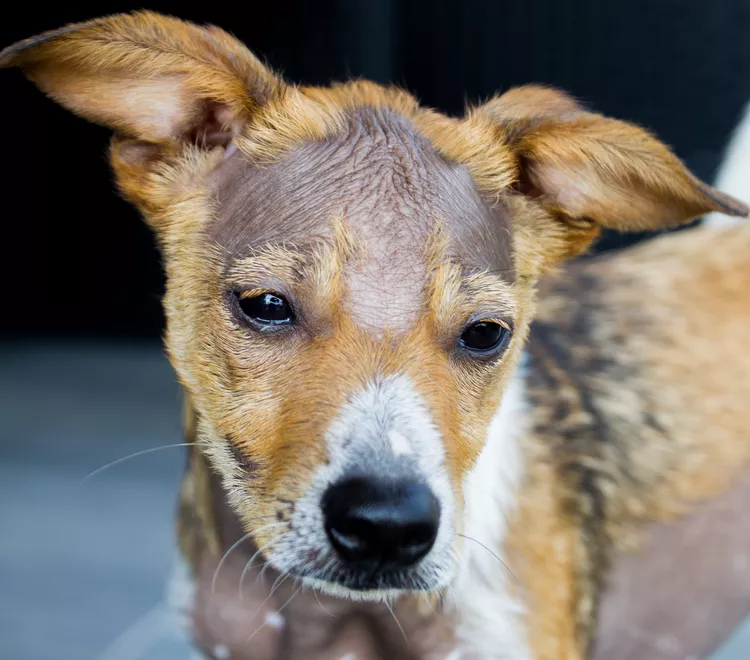

Alopecia is a medical term that refers to baldness or hair loss in areas that normally are hairy. There are many reasons a dog can develop alopecia, including allergies, skin infections, parasites including fleas or mange mites, overgrooming, lack of protein in the diet, and genetics. Depending on the cause, alopecia might be a temporary condition that can be treated, or it might be a permanent condition. Luckily, although it can be unsightly, alopecia is generally not part of a life-threatening condition, and your dog can usually lead a normal, happy life even without all of its fur.
While any dog can develop alopecia that stems from external factors such as mange, skin infections, or behavioral issues, certain breeds are more prone to inherited types of alopecia. Dachshunds, Chihuahuas, standard poodles, and Bernese mountain dogs are just a few of the breeds prone to genetic types of alopecia.
Alopecia is the medical term for hair loss or baldness. Many different types of alopecia affect dogs. With most types of alopecia, the dog's fur loss is temporary and hair growth resumes once the root cause is treated. However, inherited forms of alopecia are sometimes permanent or recurring conditions.
Depending on the cause of the alopecia, the dog might lose most of the fur on its body, but more often, alopecia leads to partial hair loss in the form of localized bald spots, symmetrical hair loss on one or both sides of the body, or fur that looks thin and moth-eaten.
Alopecia can affect any part of your dog's body, but most often appears on the ears, the top of the head, the belly, or the flanks.
The most obvious symptom of alopecia is hair loss, but other symptoms can accompany this condition, depending on the cause.
Alopecia that's caused by a hereditary or hormonal issue often has no symptoms beyond the changes to the dog's coat. However, when hair loss stems from an infestation of parasites, such as fleas or mange mites, a fungal or bacterial infection in the skin, such as ringworm, or allergies, your dog will often be itchy and scratch excessively.
Damaged skin tends to accompany the itchy forms of alopecia. You'll see dandruff or flakiness on your dog's skin and might note reddened or darkened skin, as well. If the inflammation is severe, there might be crusty or weeping spots on the skin. Usually, your dog will lick, scratch, or rub at the irritated areas to gain relief from the discomfort.
Alopecia can occur for a number of reasons, but causes are typically lumped into two categories: congenital or acquired. Congenital alopecia means the dog is born with hair follicles that do not develop normally, usually due to genetics. Symptoms of these types of alopecia can appear when the dog is still a puppy or later in young adulthood.
Acquired alopecia means the dog was born with a normal coat and normal hair follicles, but now has areas of baldness or hair loss due to damage to the hair follicles, issues with the hair shaft itself, or a slowdown in the normal hair-growth cycle.
Many causes of alopecia have specific names, while others are simply symptoms of another illness or condition. Some named types of alopecia include:
Alopecia can also occur due to parasites such as mites or fleas, environmental or food allergies, bacterial or fungal infections, hormonal issues such as low thyroid hormone (hypothyroidism) or high cortisol (Cushing's disease), some tumors, topical medications, and even seasonal fluctuations.
Certain breeds of dogs are predisposed to developing various types of congenital alopecia. Breeds that are commonly affected by different types of alopecia include:
If your dog develops bald spots or thinning of its coat, one of your veterinarian's first questions is likely to be whether or not you have observed signs of itchiness, such as scratching excessively. Itchiness typically indicates an inflammatory cause of alopecia or a response to food or environmental allergies. In these cases, your vet will look for signs of skin infections from yeast, ringworm, or bacteria and also examine the dog for signs of pest infestations, including fleas or mange mites.
Along with the physical examination, your vet might order skin scrapings or biopsies of the affected areas for microscopic examination, which can reveal typical changes associated with inflammation. Blood tests can sometimes reveal an increase in certain types of white blood cells that indicate allergies.
If your dog is not itchy, the veterinarian will likely order blood tests to check for abnormalities with the dog's thyroid, as well as blood tests that give an impression of the dog's overall health. The vet will also carry out a full physical examination, considering the symmetry of the bald spots, their location, changes to the underlying skin, and the appearance of the remaining hairs.
If your veterinarian is unable to decisively diagnose the cause of the alopecia, they might refer you to a veterinary dermatologist. However, it is not uncommon for alopecia to be simply diagnosed as idiopathic, meaning the cause is unknown.
The treatment for alopecia in dogs will vary based on the underlying reason for the hair loss. If the problem is due to a skin infection or irritation, the treatment will involve topical or oral forms of anti-parasitics, antibiotics, antifungals, or anti-inflammatory medications.
If the alopecia is due to thyroid or adrenal disorders, treatment to relieve or reverse the hormonal imbalance will usually also result in renewed hair growth. If allergies are the source of the problem, then removing the trigger—often it's a food—as well as giving the dog antihistamine medications can bring relief from the itching that caused the dog to scratch away at its fur.
Unfortunately, many forms of congenital alopecia do not have effective treatments, other than keeping the dog's skin moisturized to help avoid dryness or flakiness.
Although many forms of alopecia cannot be cured or treated, they do not shorten a dog's life or affect the quality of that life. For the most part, alopecia is a cosmetic issue that can be unsightly but won't prevent your pet from leading a happy and otherwise healthy life.
Some types of alopecia are preventable while others are out of a dog owner's control. Using parasite control and making sure any hair accessories are not applied too tightly are the best ways to prevent these avoidable types of alopecia. Other types of alopecia that are due to a genetic or auto-immune cause are not preventable but may be lessened for future generations with selective breeding.
Hair loss itself is not contagious, but ringworm, which is one cause of alopecia, is contagious to humans and other pets in the home, as are many types of mange mites. If your dog's alopecia is due to one of these causes, you'll need to take precautions against the spread of infection by washing the dog's bedding, keeping the infected dog separated from other pets in the home, and taking care to wash your hands thoroughly after petting your dog or applying medications to its skin.
Tumors, Growths, and Cysts in Dogs
Tumors, lumps, growths, or cysts are commonly found on dogs. Learn the causes, treatments, and preventative measures.
Eye Injuries and Infections in Dogs
Dogs can suffer eye injuries that range from mildly irritating to serious medical emergencies. Learn the causes, treatment, and prevention.
Vestibular Disease in Dogs
Vestibular disease affects a dog's balance and eye movements. Find out about the signs, causes, and treatment of vestibular disease in dogs.
Is Acetaminophen Safe for Dogs?
Acetaminophen is used by humans for pain and fever relief, but is it safe for dogs? Here's what you need to know before giving your dog acetaminophen.
Can Dogs Eat Zucchini? Everything to Know About This Hardy Summer Squash
Zucchini is a nutritious food that's safe for dogs to eat in moderation. This low-calorie, high-fiber vegetable can be incorporated as a healthy treat in a dog's balanced diet. Learn more about its health benefits, potential risks, and how to prepare it.
Can Dogs Eat Popcorn? What You Need to Know for Movie Night
Dogs can eat popcorn, but there are safety concerns. Find out how to safely feed your dog popcorn and what you should do if you're concerned.
65 Irish Cat Names
Irish cat names can pay homage to historical places, local cuisine, famous Irish actors and musicians, or other wonderful aspects of the Emerald Isle.
46 Egyptian Cat Names
Whether inspired by notable Egyptian deities, locales, or pharaohs, Egyptian cat names can bring out the divinity of your noble feline companion.
Are Ant Traps Safe for Cats?
Here's how to know if ant traps are safe for cats and how to keep yours free from harm if you have an ant problem.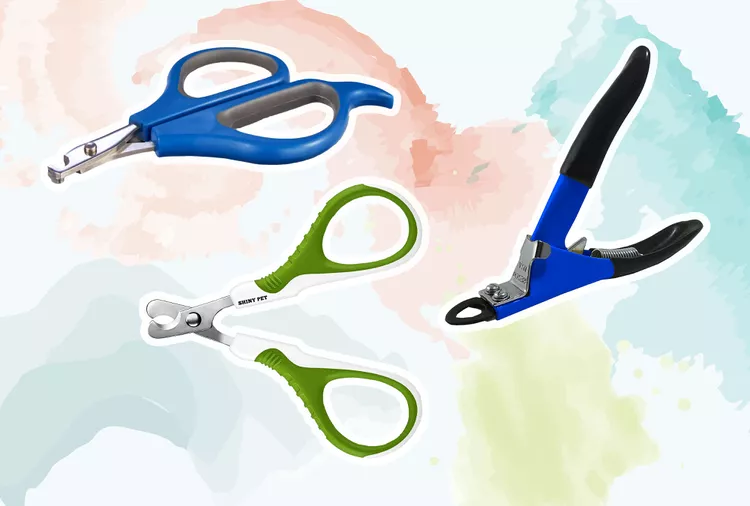
The 6 Best Cat Nail Clippers of 2024 for a Safe Trim
Clipping your cat's nails can save your furniture and keep your kitty comfortable. We asked veterinarians for their cat nail clipper recommendations.
Is Neosporin Safe for Cats?
A brief summary of concerns a cat owner should be aware of before putting Neosporin on their cat, plus tips for things they can use at home instead.
Can Cats Eat Strawberries? How to Safely Share This Summer Berry
Although cats are primarily meat eaters, strawberries may be an interesting and tasty snack for your feline friend. Find out the risks of feeding strawberries to cats and how to safely let your cat enjoy this fruit.
Cute Pictures & Facts About Calico Cats & Kittens
Learn fascinating facts about calico cats, including photos, the genetics behind this color combination, and common folklore and traditions.
12 Most Popular Cat Breeds for Feline Lovers
These 12 cat breeds, like the Siamese and Sphynx, are known for their unique appearances and personalities. Learn what makes them so popular.
Balinese: Cat Breed Profile, Characteristics & Care
The Balinese cat is playful, sociable, elegant, intelligent, and a touch on the vocal side. Learn about the Balinese, including appearance, temperament, health, and care needs.
Why Cats Don't Always Cover Their Poop
Cats may not cover their poop for a few different reasons, including being territorial, sending a message to their owner, and not liking the litter.
Cavapoo: Dog Breed Characteristics & Care
The Cavapoo is a hybrid of the Cavalier King Charles spaniel and a toy or miniature poodle. Learn why these teddy-bear-looking dogs make the perfect addition to your family.
Why Dogs Eat Poop and How to Stop Them
Is your dog eating poop? Some dogs do this because of stress or illness. Learn how to prevent stool eating, or coprophagia, in dogs.
Can Dogs Get Depression? How to Help Your Sad Dog
Can dogs get depression? Learn about the signs of depression in dogs and find out how to help your sad dog.
4 Reasons Why Your Dog Licks Their Butt
Butt-licking in dogs can be a part of normal grooming, but excessive butt-licking is not normal. Read about the most common reasons for this behavior.